Hearing is one of our most precious senses, allowing us to engage with the world and connect with others. However, like any part of our body, our hearing can face challenges over time. The good news is that hearing loss prevention, diagnosis, and management have seen remarkable advancements in recent years, making it easier for individuals to maintain and improve their hearing. In this article, we will explore what you can expect at your hearing exam, shedding light on the latest innovations in hearing healthcare, the importance of early detection, and the potential future of hearing interventions.
The Importance of Early Detection
Hearing loss is often a gradual process, which can lead individuals to underestimate its impact on their daily lives. According to the World Health Organization, over 5% of the world’s population suffers from disabling hearing loss. Early detection is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention and prevents the worsening of hearing loss. If you suspect any hearing issues or notice signs such as difficulty understanding conversations or ringing in your ears (tinnitus), it’s vital to seek professional help promptly.
The Hearing Exam Process
Case History and Discussion:
Your hearing healthcare provider will start by discussing your medical history and any specific concerns you may have. This conversation helps the audiologist or hearing specialist understand your unique situation, which can guide the examination and recommendations.
Physical Examination:
A visual inspection of your ears is the next step. This examination checks for any visible issues, such as earwax buildup or physical abnormalities, which could affect your hearing.
Audiometric Testing:
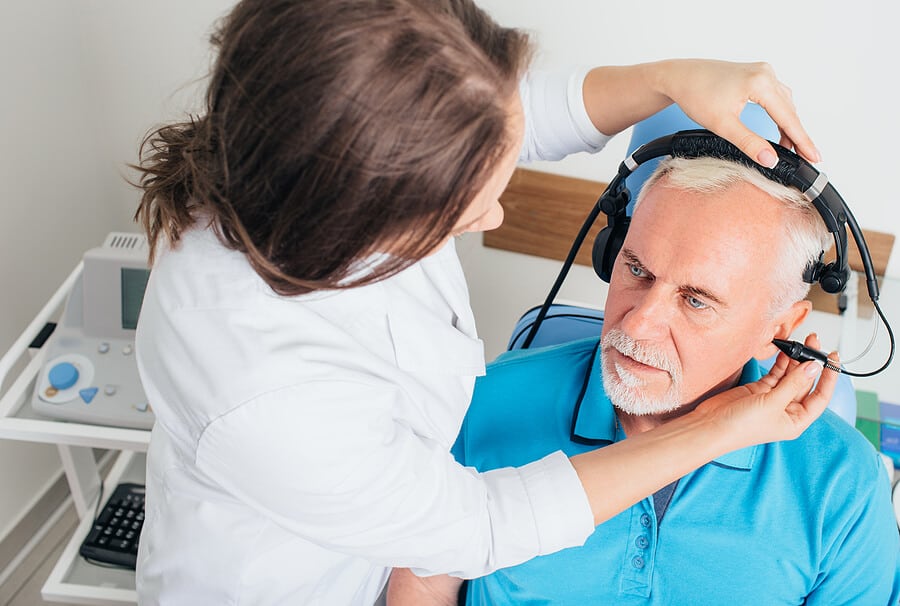
Audiometric tests are the core of a hearing exam. These tests evaluate your ability to hear different pitches and volumes of sound. The most common audiometric test is pure-tone audiometry, where you listen to a series of beeps through headphones and indicate when you can hear them. This helps determine the degree and type of hearing loss, if present.
Speech Audiometry:
In this test, you will be asked to repeat words or sentences at different volumes. Speech audiometry assesses your ability to understand speech, which is often more relevant in real-life situations than just hearing beeps.
Tympanometry:
This test examines the movement of your eardrum in response to changes in air pressure. It helps identify problems in the middle ear, such as fluid buildup or issues with the eardrum.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) and Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Tests:
These tests are sometimes conducted to gain more insight into the functioning of the inner ear and the auditory nerve. OAE measures the sound waves produced by the inner ear, while ABR evaluates the brain’s response to sound.
Latest Advancements in Hearing Healthcare
Advancements in hearing healthcare have brought about a range of innovative solutions that offer hope and improved quality of life for those with hearing loss. Here are some notable developments:
Digital Hearing Aids:
Modern hearing aids have become highly sophisticated. They use digital signal processing to enhance sound quality, reduce background noise, and adapt to different listening environments. Some are even Bluetooth-compatible, allowing users to connect to smartphones and other devices.
Cochlear Implants:
For those with severe or profound hearing loss, cochlear implants are a game-changer. These surgically implanted devices stimulate the auditory nerve directly, restoring hearing capabilities to many who were previously unable to benefit from hearing aids.
Teleaudiology:
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of teleaudiology, enabling remote hearing healthcare services. This allows individuals to have their hearing checked and receive counseling without leaving their homes.
Hearing Health Apps:
Numerous smartphone apps are designed to help individuals monitor their hearing health and track changes over time. These can be valuable tools for early detection and management.
The Future of Hearing Interventions
While the present offers impressive advancements in hearing healthcare, the future is equally promising. Researchers are exploring groundbreaking interventions that may change the way we perceive and manage hearing loss:
Gene Therapy:
Gene therapy holds the potential to correct genetic hearing loss. Scientists are investigating how to deliver therapeutic genes to the inner ear to restore or preserve hearing function.
Hair Cell Regeneration:
Hearing loss is often caused by damage to the hair cells in the inner ear. Regenerative medicine aims to regrow these cells, potentially restoring hearing in people with sensorineural hearing loss.
Neuroprotection:
Researchers are developing drugs that protect the auditory nerve from damage due to loud noise, aging, or other factors. These drugs could potentially slow or even prevent hearing loss.
Your hearing health is too important to neglect. Regular hearing exams are essential for early detection and intervention, potentially saving your hearing and improving your overall quality of life. With the latest advancements in hearing healthcare, there are more options than ever for managing hearing loss, ensuring that you can continue to enjoy the sounds of life. As technology and research continue to advance, the future holds even more promise for individuals with hearing difficulties. Whether through gene therapy, regenerative medicine, or neuroprotective drugs, the path to better hearing is brighter than ever. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help and stay informed about the latest developments in hearing healthcare, as it may make all the difference in your journey to better hearing and an improved quality of life.